前言
我的网站证书三个月更新一次.由于懒癌, 现在连证书都不想手动部署了, 于是决定写一个脚本配合 acme 自动更新我的网站证书
本文默认读者会使用acme签发域名证书, 环境为已经签发了一次证书后的linux服务器.
证书关联与需求分析
我有两个域名
一个域名证书在七牛云cdn上会用到
另一个域名在nginx上会使用到
于是流程分为
1.acme签发证书
2.七牛云上传证书
3.七牛云部署证书
4.将证书存储到nginx配置文件指定的ssl证书位置
5.nginx重启
七牛云自动部署
根据官方文档需要接口
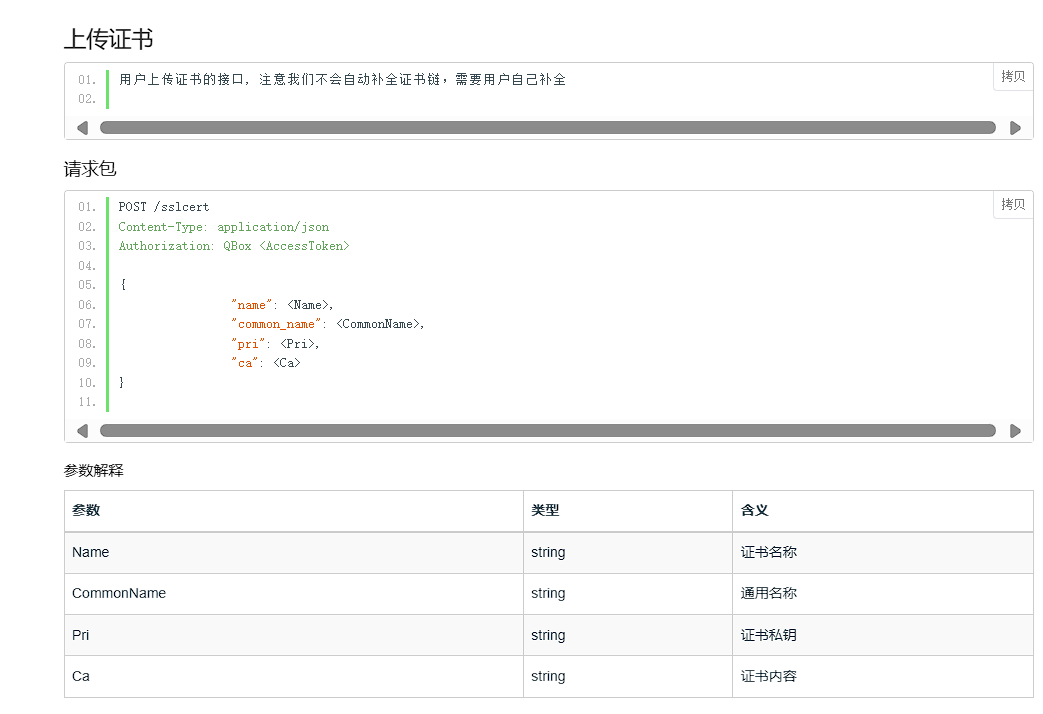
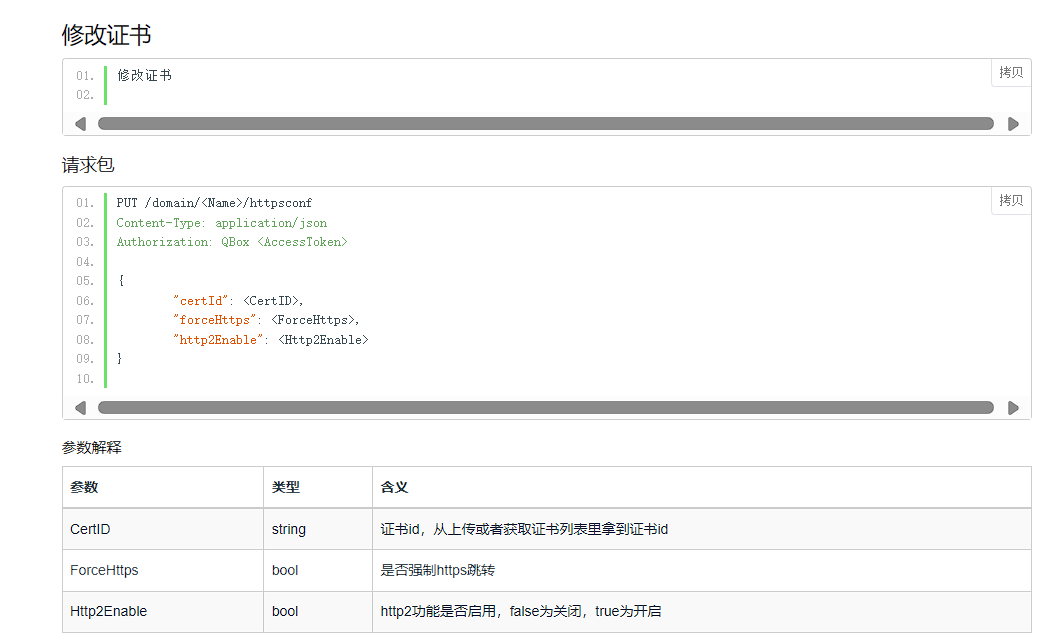
这里我考虑的是运用七牛云官方python sdk一部分.官方sdk不支持这两个功能,需要手动获取token后调用接口
这里可以看七牛云官方python sdk的源码, auth部分, 位于lib/sites-packages/qiniu/auth.py
先配置虚拟环境然后安装应该就不用我说了
python -m venv .venv && .venv/bin/pip install qiniu
关键代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
class Auth(object):
"""七牛安全机制类
该类主要内容是七牛上传凭证、下载凭证、管理凭证三种凭证的签名接口的实现,以及回调验证。
Attributes:
__access_key: 账号密钥对中的accessKey,详见 https://portal.qiniu.com/user/key
__secret_key: 账号密钥对重的secretKey,详见 https://portal.qiniu.com/user/key
"""
def __init__(self, access_key, secret_key, disable_qiniu_timestamp_signature=None):
"""初始化Auth类"""
self.__checkKey(access_key, secret_key)
self.__access_key = access_key
self.__secret_key = b(secret_key)
self.disable_qiniu_timestamp_signature = disable_qiniu_timestamp_signature
def get_access_key(self):
return self.__access_key
def get_secret_key(self):
return self.__secret_key
def __token(self, data):
data = b(data)
hashed = hmac.new(self.__secret_key, data, sha1)
return urlsafe_base64_encode(hashed.digest())
def token(self, data):
return '{0}:{1}'.format(self.__access_key, self.__token(data))
def token_of_request(self, url, body=None, content_type=None):
"""带请求体的签名(本质上是管理凭证的签名)
Args:
url: 待签名请求的url
body: 待签名请求的body
content_type: 待签名请求的body的Content-Type
Returns:
管理凭证
"""
parsed_url = urlparse(url)
query = parsed_url.query
path = parsed_url.path
data = path
if query != '':
data = ''.join([data, '?', query])
data = ''.join([data, "\n"])
if body:
mimes = [
'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
]
if content_type in mimes:
data += body
return '{0}:{1}'.format(self.__access_key, self.__token(data))
|
那么获取token的示例就是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
from qiniu import Auth
import requests
AccessKey = "your_access_key"
SecretKey = "your_access_secret_key"
q = Auth(access_key=AccessKey, secret_key=SecretKey)
def uploadCert(key, crt):
host = "api.qiniu.com"
method = "POST"
data = {
"name": str(uuid.uuid1()),
"common_name": "*.voidval.com",
"pri": key,
"ca": crt
}
header = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
path = "/sslcert"
url = f"https://{host}{path}"
token = q.token_of_request(url=url, body=data, content_type="application/json")
header['Authorization'] = f"QBox {token}"
resp = requests.post(url, json=data, headers=header, verify=False)
print(resp.json())
return resp.json()['certID']
|
同理写出刷新域名证书代码即可
完整代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
|
## @Time : 2024/12/12 13:59
## @Author : TwoOnefour
## @File : refreshcert.py
import hmac
import hashlib
import base64
import json
import requests
import uuid
import urllib.parse
import urllib3
from qiniu import Auth
AccessKey = "xxxxx"
SecretKey = "xxxxxx"
q = Auth(access_key=AccessKey, secret_key=SecretKey)
urllib3.disable_warnings()
def uploadCert(key, crt):
host = "api.qiniu.com"
method = "POST"
data = {
"name": str(uuid.uuid1()),
"common_name": "*.pursuecode.cn",
"pri": key,
"ca": crt
}
header = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
path = "/sslcert"
url = f"https://{host}{path}"
# token = getAuthToken(method=method, path=path, body=data, header=header, host=host)
token = q.token_of_request(url=url, body=data, content_type="application/json")
header['Authorization'] = f"QBox {token}"
resp = requests.post(url, json=data, headers=header, verify=False)
print(resp.json())
return resp.json()['certID']
def setcert(CertID):
host = "api.qiniu.com"
method = "PUT"
header = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
domains = [
"www.example.com",
"bucket.example.com"
]
paths = [
f"/domain/{domain}/httpsconf" for domain in domains
]
data = {
"certId": CertID,
"forceHttps": True,
"http2Enable": True
}
for path in paths:
url = f"https://{host}{path}"
token = q.token_of_request(url=url, body=data, content_type="application/json")
header['Authorization'] = f"QBox {token}"
resp = requests.put(url, headers=header, json=data, verify=False)
print(resp.json())
if __name__ == "__main__":
cer = None
key = None
with open(r"/root/.acme.sh/*.example.com/fullchain.cer") as f:
cer = f.read().strip()
with open(r"/root/.acme.sh/*.example.com/_.example.com.key") as f:
key = f.read().strip()
certid = uploadCert(crt=cer, key=key)
setcert(certid)
|
这里后面open语句填acme生成得到的证书路径,将此python路径记住备用,我这里是/root/qiniu/refreshcert.py
acme签发证书
如果你已经运行过一次acme且成功签发证书,在证书签发的文件夹可以找到*.example.com.conf这个配置
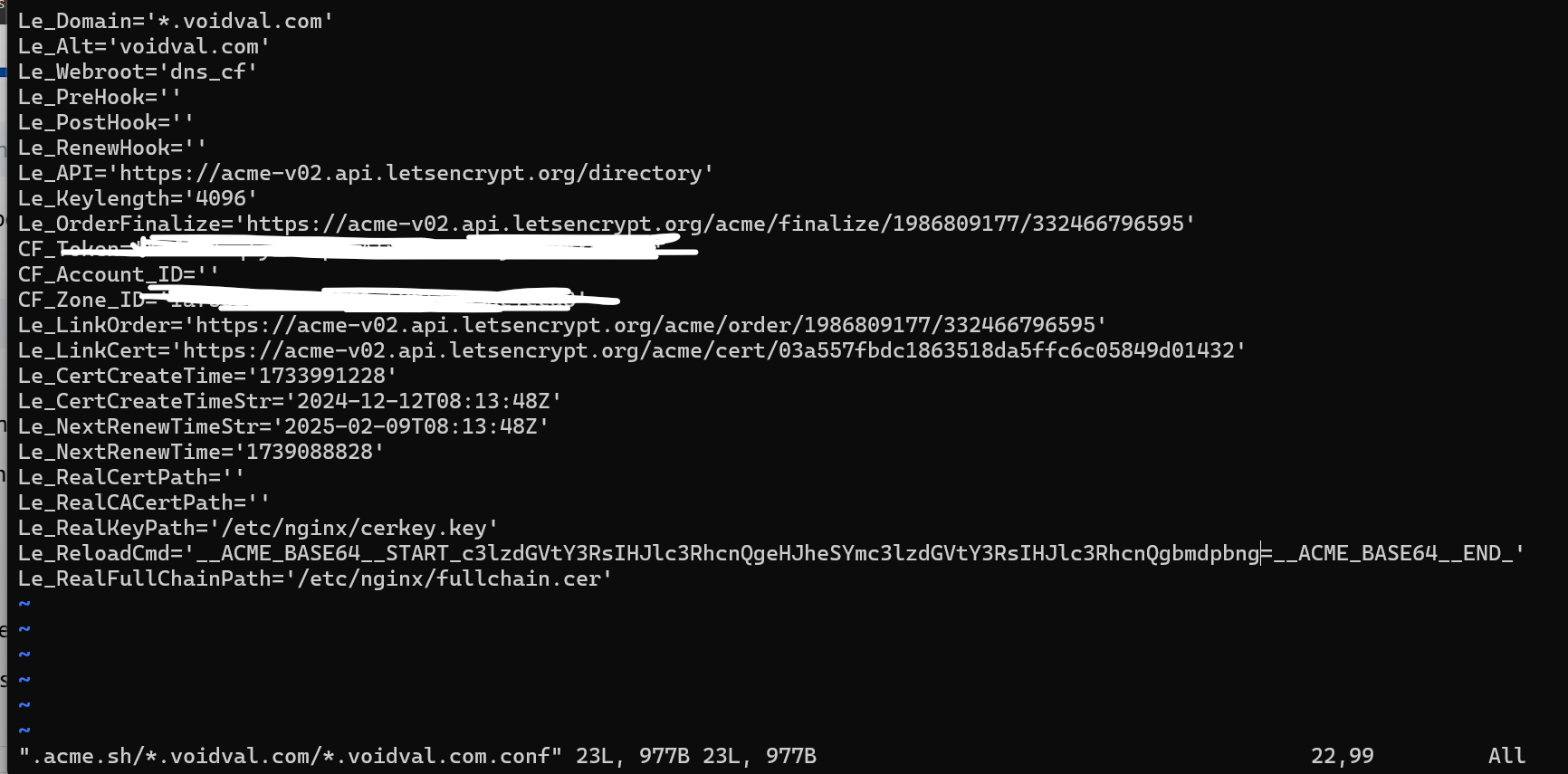
这里主要是看Le_reloadCmd和Le_realKeyPath
-
Le_reloadCmd 是在执行完acme签发证书命令后会执行的命令, 这里是经过base64编码的, 格式如下
__ACME_BASE64__START_base64(cmd_plain_string)__ACME_BASE64__END_
也就是说要将命令经过一次base64编码
例如我的需求是systemctl restart nginx
将他编码为base64后就是
c3lzdGVtY3RsIHJlc3RhcnQgeHJheSYmc3lzdGVtY3RsIHJlc3RhcnQgbmdpbng=
一整串就是
__ACME_BASE64__START_c3lzdGVtY3RsIHJlc3RhcnQgeHJheSYmc3lzdGVtY3RsIHJlc3RhcnQgbmdpbng=__ACME_BASE64__END_
-
Le_realKeyPath 是acme签发证书的文件位置
这里就把nginx的ssl证书位置填上对应的即可
比如我的证书配置是这样的
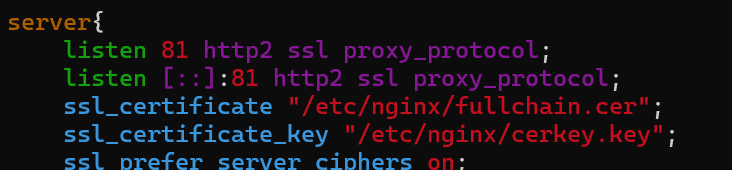
那么 Le_realKeyPath就填/etc/nginx/cerkey.key
接下来crontab中一般会含有如下语句,这是acme用来自动刷新证书的
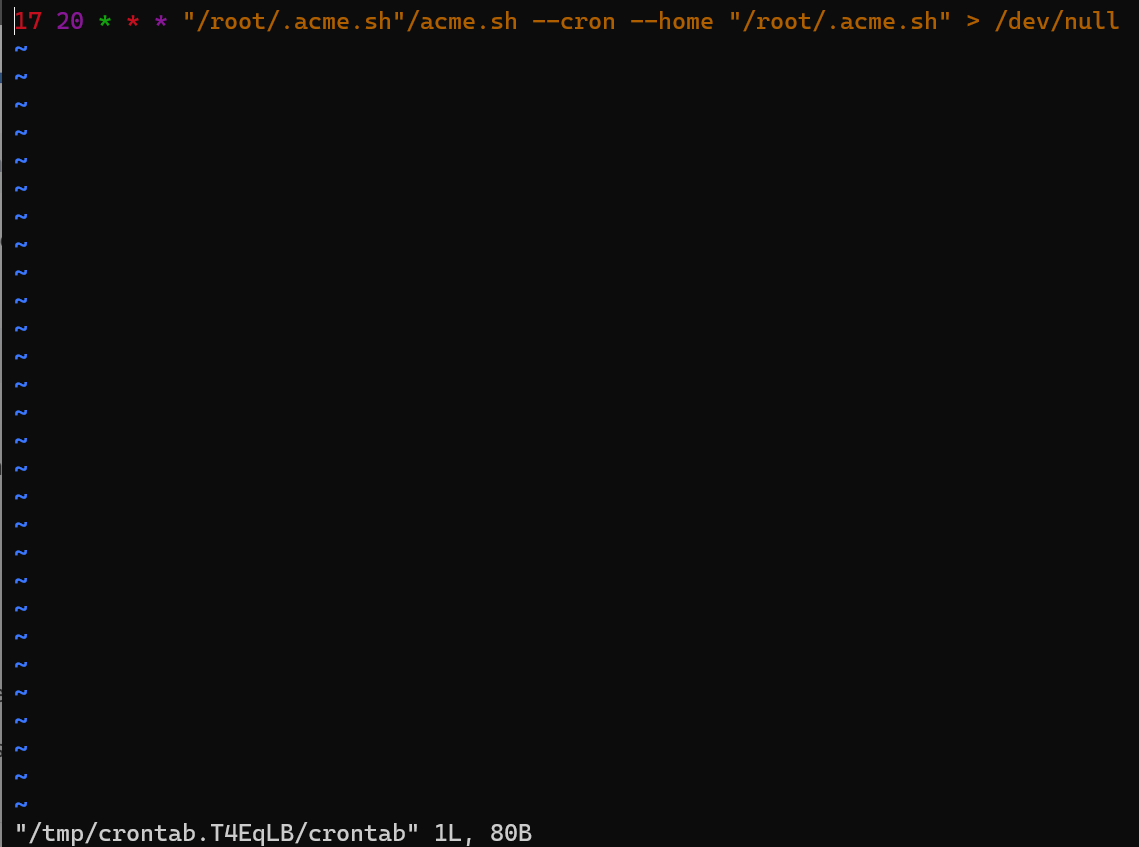
这样就部署好了,可以尝试运行一下crontab里写的这串命令
"/root/.acme.sh"/acme.sh --cron --home "/root/.acme.sh" --force
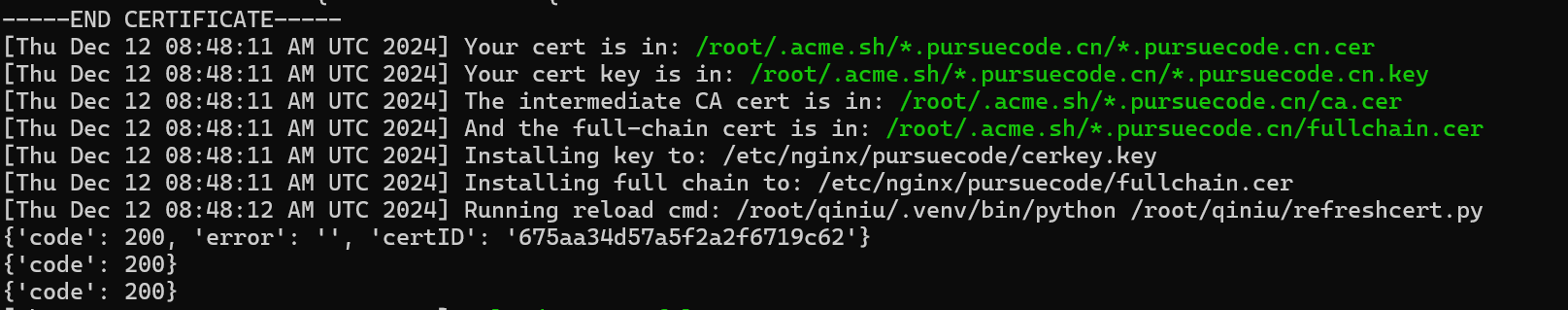
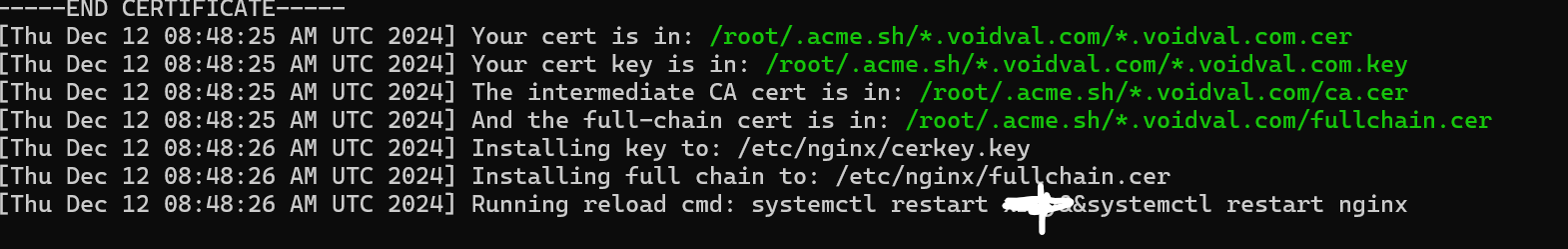
至此懒人部署证书逻辑大功告成







